
On radio last week, Glenn discussed California’s bullet train project, which is a complete and total joke. Billions of dollars, decades in the making, and what do they have?
A hopeless boondoggle that’s become the poster child for government waste. Politicians just leaf-blowing your tax dollars into a black hole.
Rewind to the late 1800s, to a man named James J. Hill and his Great Northern Railroad – the polar opposite of California’s embarrassment. His story is about American grit, private enterprise, and it’s proof that when you keep the government’s hands off, you can get real results.
James J. Hill didn’t just build a railroad; he built a legacy that shames every federally funded train wreck of his era.
Picture this: it’s the 1870s, and railroads are the arteries of America’s growth. But most transcontinental lines, like the Union Pacific and Central Pacific, are swimming in federal cash through massive loans and land grants. They would get up to 20 square miles of land PER MILE of track, plus loans of $16,000 to $48,000 per mile, depending on the terrain. Naturally, those railroads were bloated, mismanaged, and built as fast as possible to grab the government subsidies. Since they got a pile of federal cash for every mile they completed, they often picked less efficient routes. The cheap and fast construction also meant the tracks were in constant disrepair and had to be re-laid. By the Financial Panic of 1893, they were bankrupt, bleeding money, and begging for bailouts.
Enter James J. Hill. This guy was different. He didn’t want Uncle Sam’s handouts. He spent three years researching the bankrupt St. Paul and Pacific Railroad, ensuring it could be profitable with strategic expansion. In 1878, Hill and his investment partners bought the SP&P with their own money. No federal loans, except for a single small land grant in Minnesota, that they needed to connect their line to the Canadian Pacific Railroad. Hill carefully used profits from this line to fund further expansion, avoiding excessive debt.
By 1893, the Great Northern Railroad stretched from Minnesota all the way to Seattle, built almost entirely with private capital. Why did Hill’s Great Northern become the gold standard? First, efficiency. Hill was obsessive. He scouted routes himself, picking paths like Marias Pass – the lowest crossing of the Rockies – saving millions of dollars by avoiding tunnels. His tracks had low grades, minimal curves, and were built to last.
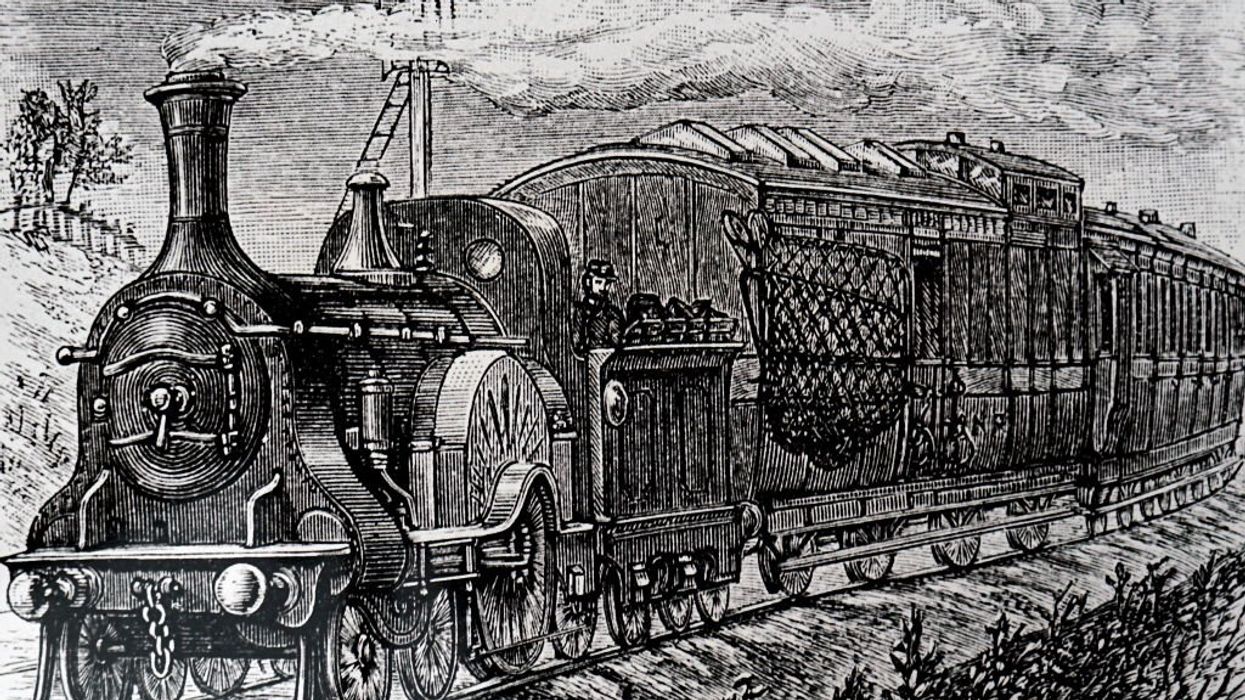
Universal History Archive / Contributor | Getty Images
Second, Hill didn’t just build tracks; he built an economy. He attracted settlers by offering cheap fares, free seeds for their farms, and even programs that taught them better farming techniques. He invested in timber, ensuring that freight kept rolling. The result? His railroad always had plenty of customers, cargo, and cash flow. The federally funded lines, on the other hand, often ran through barren land, chasing land grants, not profits.
When the Panic of 1893 hit, the Great Northern line withstood the storm – it was one of only two Western railways NOT to go bankrupt.
Hill reinvested profits, kept debt low, and outmaneuvered the government’s new rate controls that crippled his competitors. By 1901, he controlled the Northern Pacific and Burlington lines, creating an empire that still exists today, part of a merger in the 1990s that created the BNSF Railway. That is the power of private enterprise – no government bloat, just hard work and vision.
James J. Hill’s Great Northern Railroad proves what happens when you let markets, not bureaucrats, drive progress. Hill’s legacy reinforces a vital truth: keep the government out, and let builders build. That’s the American way.